Knowledge
HMG Powder Coatings recognise that there is nothing more frustrating than searching around for documents, only to find you need to register to have these. We have made the sourcing, reading and downloading of all our Safety & Technical Data Sheets only a quick click away. You will also find our regulatory statements and accreditations just as easy to find.
Resources
Technical Guidance
When you need help, you need to know you are only a few clicks away from us helping you resolve the problem.
HMG Powder Coatings are keen to be the 'Go To' web site for advice information & genuine problem solving in the application of powder coating.
-
-
-
-
Life Expectancy
ViewWe give some guidance on how long your coating system will last in a number of different environments.
Help Centre
Useful tips to overcome common issues
Mechanical & Chemical
-

Adhesion
AdhesionAdhesion can be tested using a sharp blade to create perpendicular cross cuts 1mm and 2mm apart. Very poor adhesion will be apparent as total delamination of the squares; but finer degrees of adhesion can also be discerned with reference to ISO 2409 and rated 0-5 (best to worst).
-
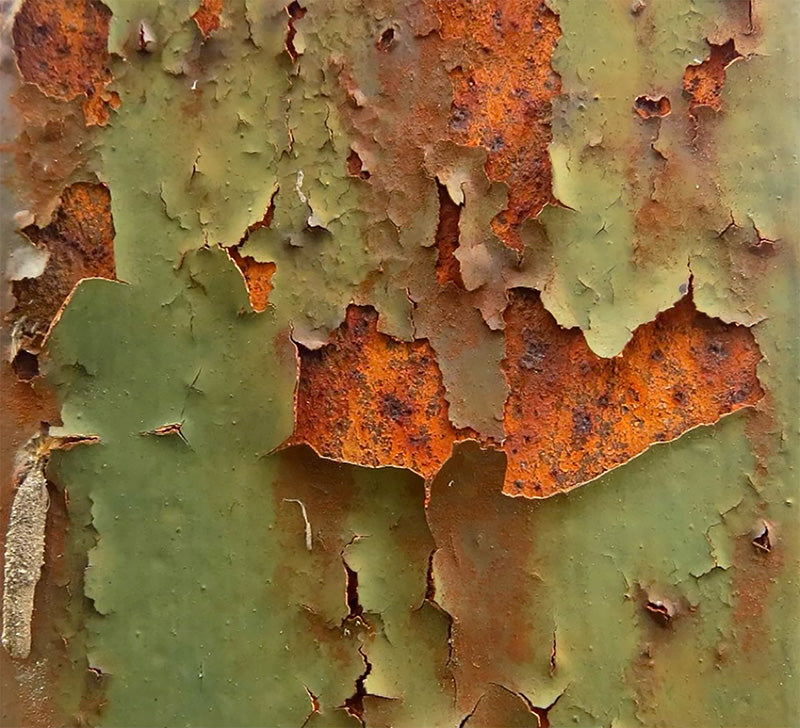

Corrosion
CorrosionCorrosion occurs under the correct environmental conditions, and usually involves the metal substrate, salts and moisture in the presence of oxygen. Corrosion will cause the delamination of the coating, usually first apparent as blistering of the coating or filiform corrosion.
-

Flexibility, Hardness and Impact Resistance
MoreMechanical tests are often carried out as part of QC process as an indicator of cure and include many testing procedures, from falling weight impact, to pencil hardness, to scratch or abrasion testing.
-

Chemical
ChemicalEvery powder coating system, polyester, epoxy, acrylic, etc, will have its own intrinsic resistance to chemical attack. A coating's resistance to chemicals can be tested in a number of ways, most usually by prolonged exposure, either a spot test or by partial submersion in the liquid chemical.
Application
-
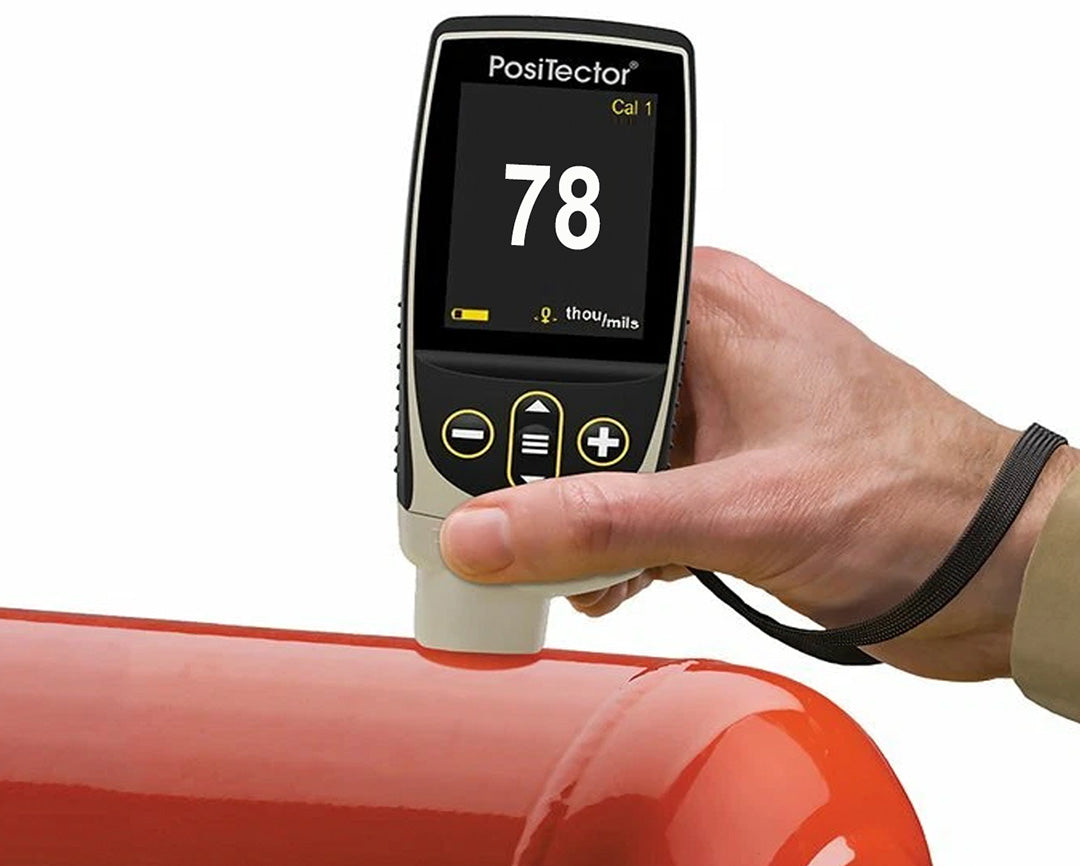
Film Thickness
Film ThicknessDry Film Thickness (DFT) is measured in microns or in mils
1 mil is approximately 25 microns. Coatings are designed with a DFT in mind and being below or above the recommended range can have undesirable results.
-
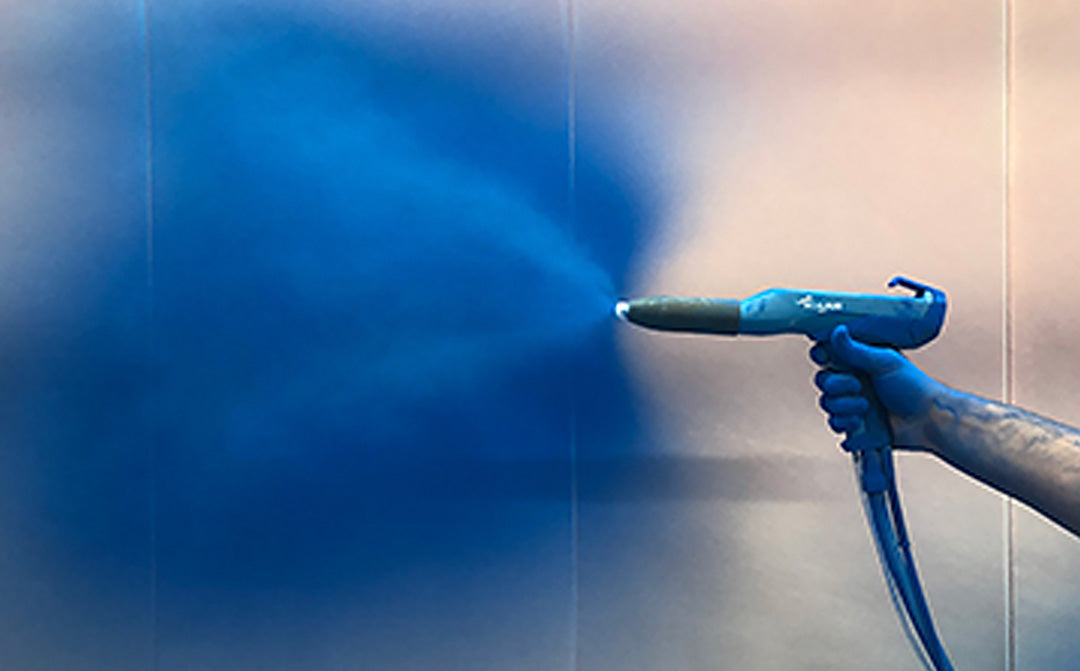

Product Coverage
CoverageCoverage may be measured in many ways: weight per area, or area per weight. More simply, where the parts being sprayed are the same, it can be measured by parts per box.
-
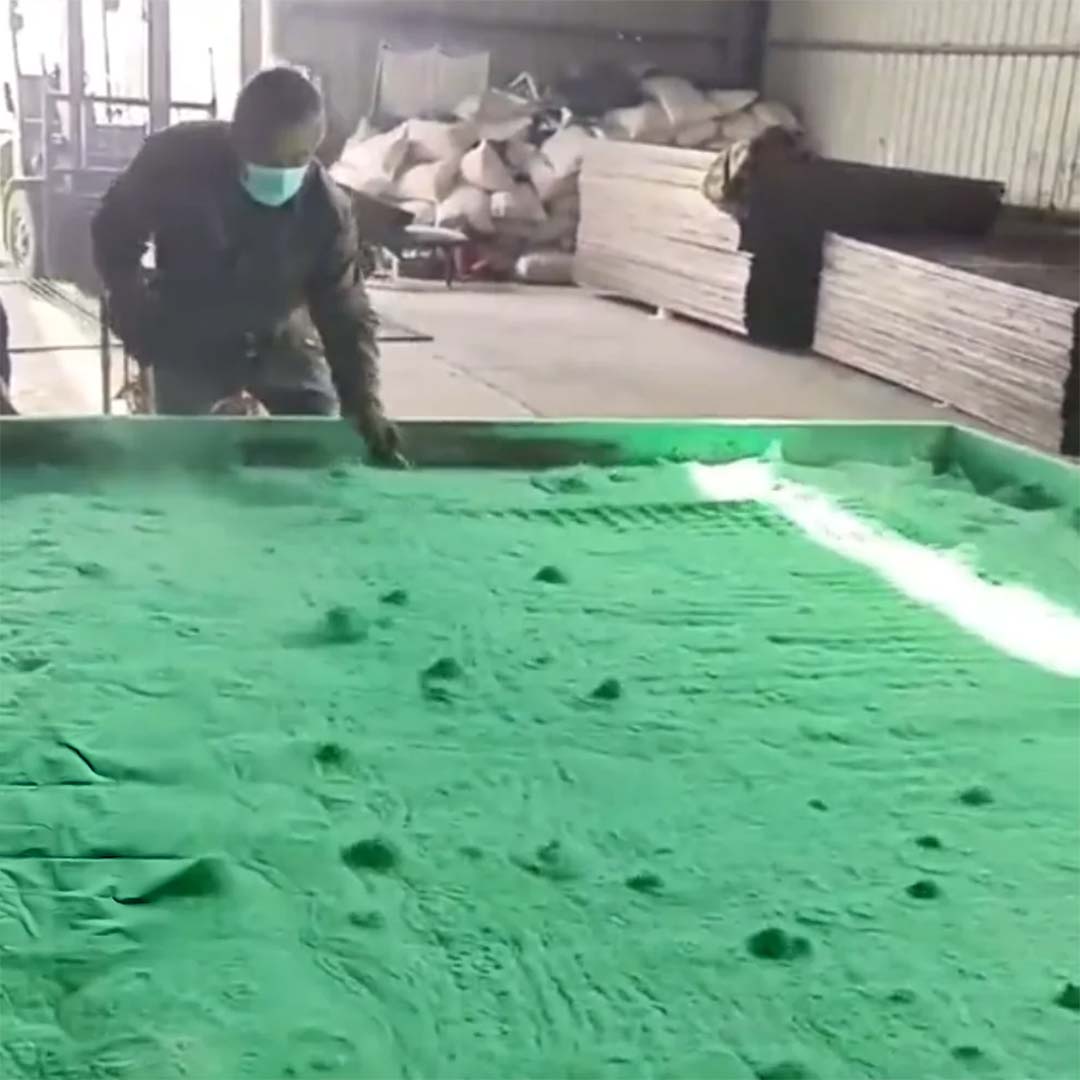

Fluidisation
FluidisationPowder is supposed to flow like water in the container; correctly fluidised powder should appear like simmering water. There are various tests for powder coating fluidity, most notably the 'Sames Test' (AFNOR) which gives a R value to a powder coating.
-
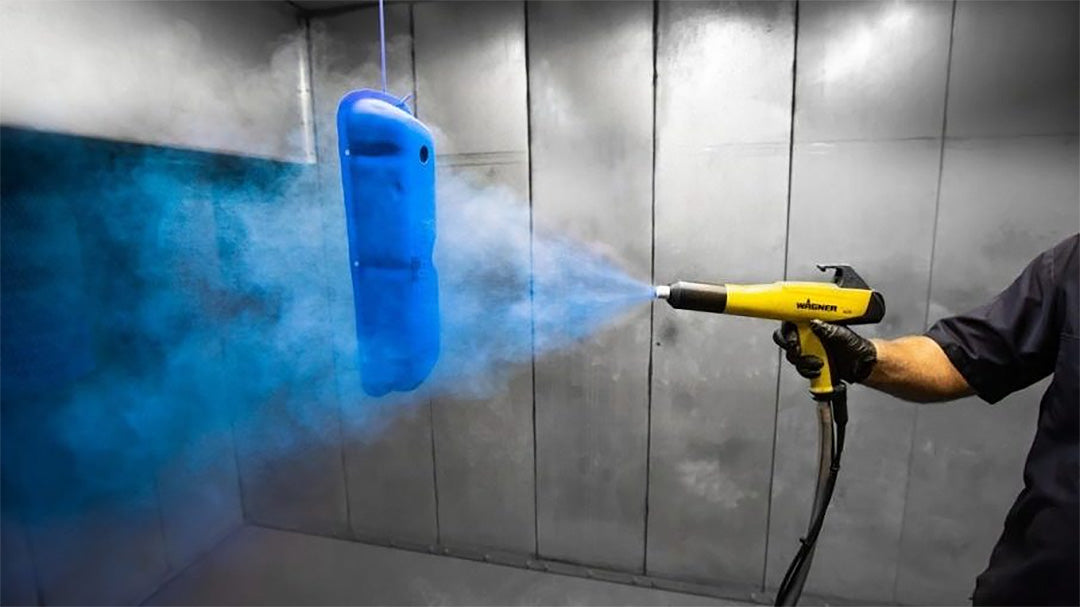

Spray Characteristics
Spray CharacteristicsDepending on the choice of nozzle, the powder coating spray pattern will be different. However all powder coating spray clouds should be an even, soft stream of powder, free from surges and spitting.
-
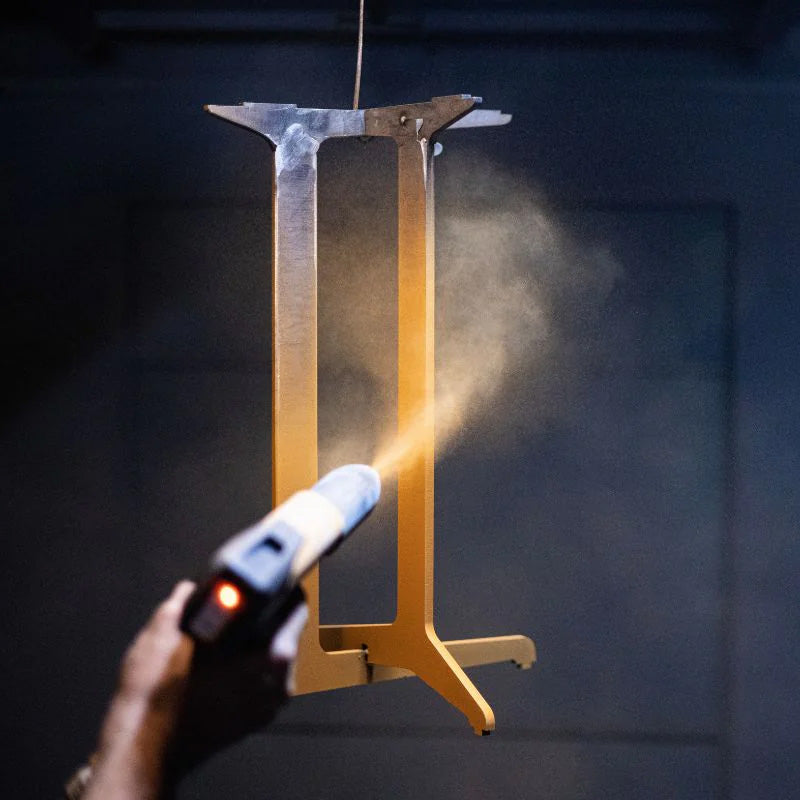

Supply Problems
Supply ProblemsFluidisation is good, but the powder is not being fed to the gun in a smooth continuous flow. These problems may be caused by blockages in the feed system, including hoses, venturi and spray gun equipment.
Coating Defects
-

-
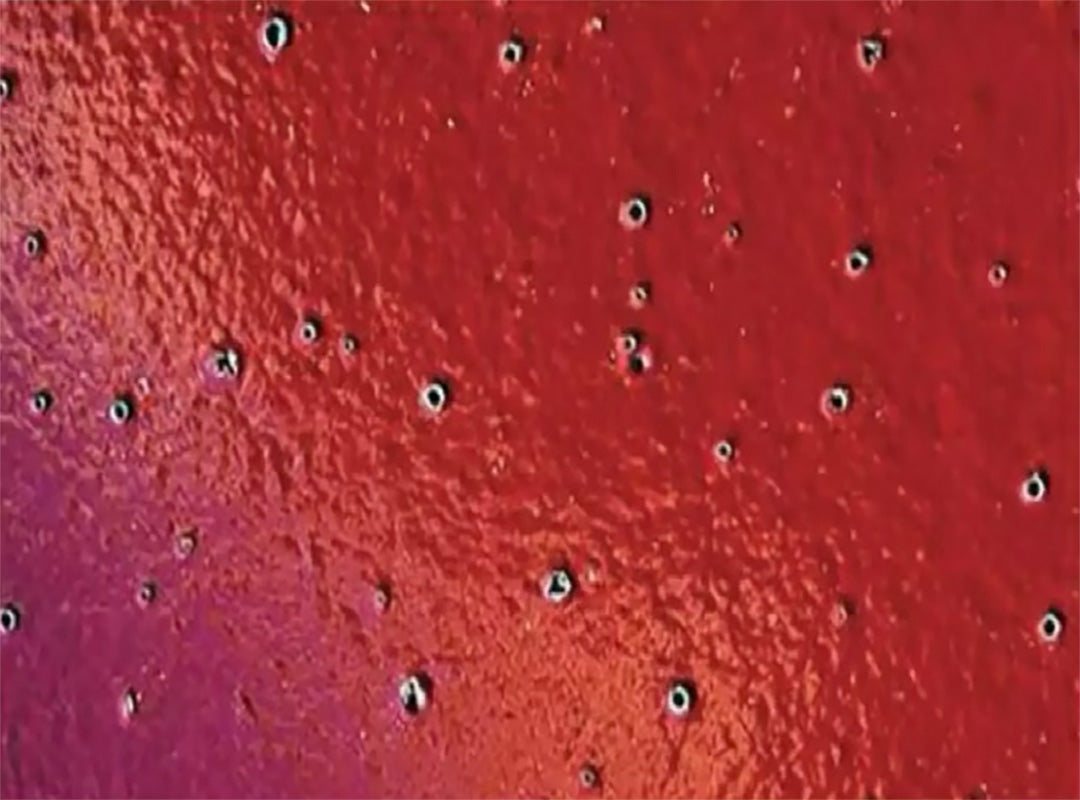
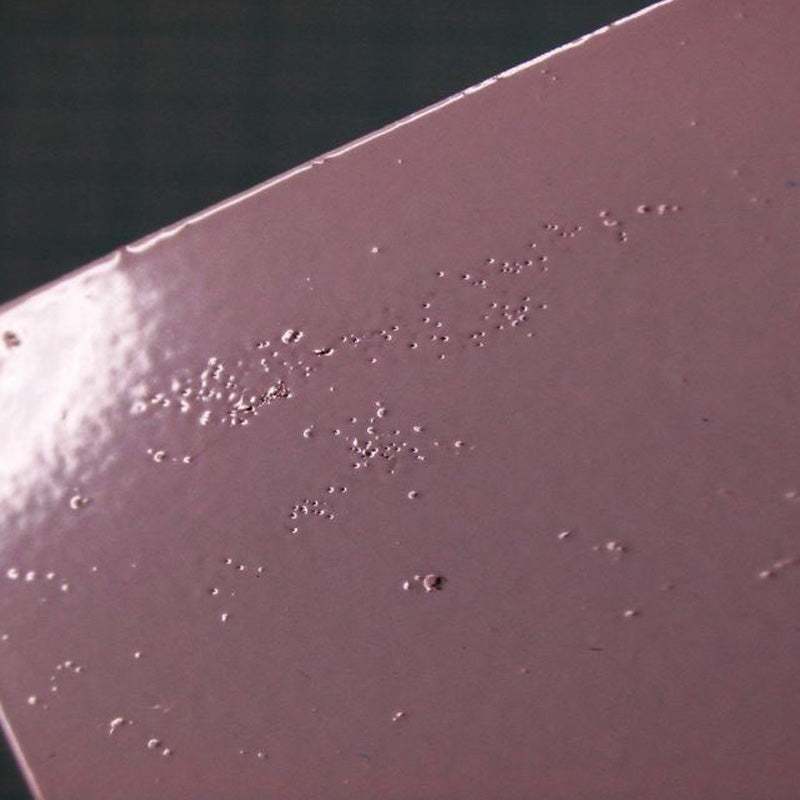
Craters
CratersAreas in the coating surface where film thickness has been precipitously reduced, potentially to the substrate surface.
-
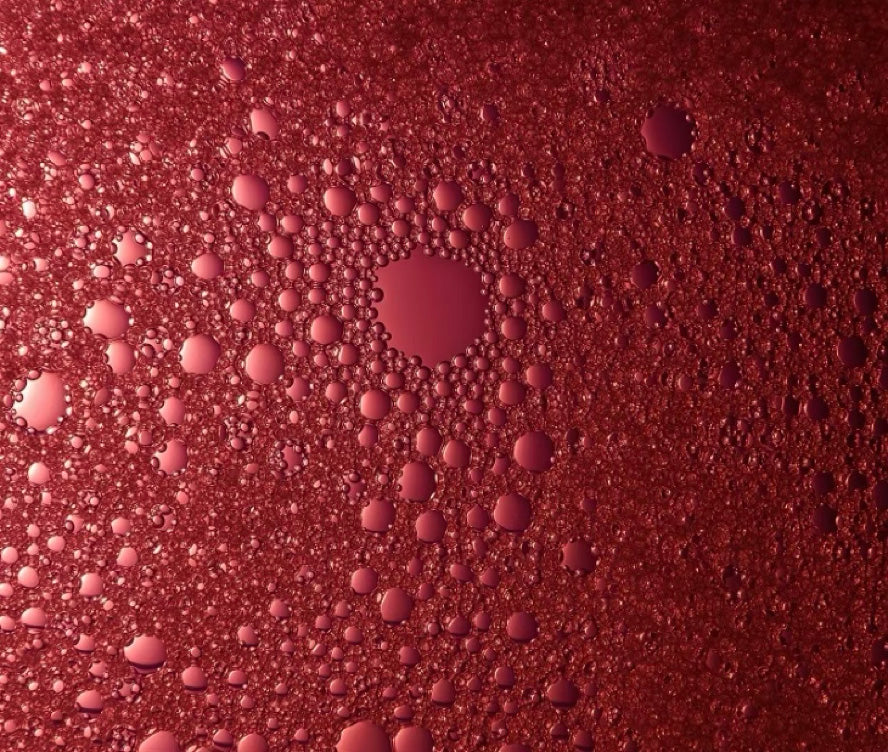
Gloss Appearance
-

Haziness
HazinessColour is a visual attribute and is often conveniently assessed qualitatively by eye under sufficient light to test the colour against the expected result (the colour 'standard'). Where a quantitative measurement is required, colour spectrophotometry is used as a tool. The light source will have a bearing on how the final colour is perceived.
-
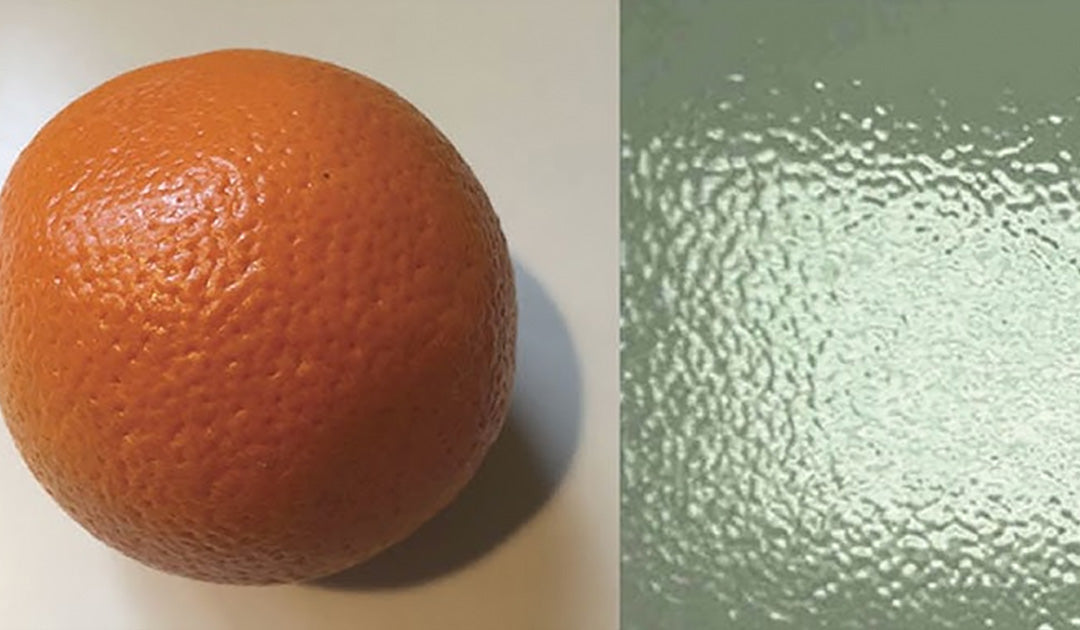

Orange Peel
Orange PeelA description of the smoothness of the coating. Where coatings are not totally level they develop a waviness in the coating, not dissimilar to an orange peel.
-

Sheen
SheenThe amount of unscattered light reflected from the surface of a coating is its gloss level. An incident angle of 60 degrees is often used, although 20 and 80 degree measurements have limited use too. Gloss level is often described as a percentage, however Gloss Units (GU) is the more accurate description.
-

Inconsistent Colour
Inconsistent ColourFor consistency, ideally a coating's film thickness ought to be the same no matter where on the part. Where build-up occurs at the edges of a part, this is called 'Picture Framing', and on flat sheets 'Striping'.















